
Long-term assets are possessions that cannot reliably be converted to cash or consumed within a year. They include investments; property, plant, and equipment (PPE), and intangibles such as patents. Retained earnings are part of shareholder equity as is any capital invested in the company. A company’s negative equity that remains prolonged can amount to balance sheet insolvency.
Examples of Shareholder Equity
Investors are looking for higher returns, but RF is a good number to use as a baseline for cost-of-equity calculations. The amount of equity awarded to investors is determined by a stock price based on the company’s valuation. The amount of the equity investment determines the ownership percentage given to the investor. This can be represented by common stock, which comes with voting rights, or preferred stock with a higher liquidation preference. Calculate the shareholder equity fund for the total assets of 250 $ and total liabilities of 140 $.
- Built to help you elevate your game at work, our courses distill complex business topics — like how to read financial statements, how to manage people, or even how to value a business — into digestible lessons.
- Current liabilities are debts typically due for repayment within one year.
- This reverse capital exchange between a company and its stockholders is known as share buybacks.
- Market analysts and investors prefer a balance between the amount of retained earnings that a company pays out to investors in the form of dividends and the amount retained to reinvest into the company.
How do you calculate shareholders’ equity?
Shareholders’ equity isn’t the sole indicator of a company’s financial health, however. It should be paired with other metrics to obtain a more holistic picture of an organization’s standing. The formula to calculate shareholders equity is equal to the difference between total assets and total liabilities. It’s a risk factor calculated by comparing the company’s rate of return with the average market rate of return (MRR). Mining and pharmaceutical companies typically have higher Betas, but they also offer higher potential returns for investors. Shareholders’ equity provides investors a glimpse into the financial health of a company.
FAQs about the cost of equity calculation
It indicates the portion of assets that belongs to shareholders instead of creditors. A high stockholders’ equity means the company has more resources to finance its growth, attract investors and increase credibility and confidence in the market. This strength reduces the company’s risk of insolvency and allows for potential investments in profitable projects. Retained earnings are reinvested in the business, not distributed as dividends, allowing for long-term returns.
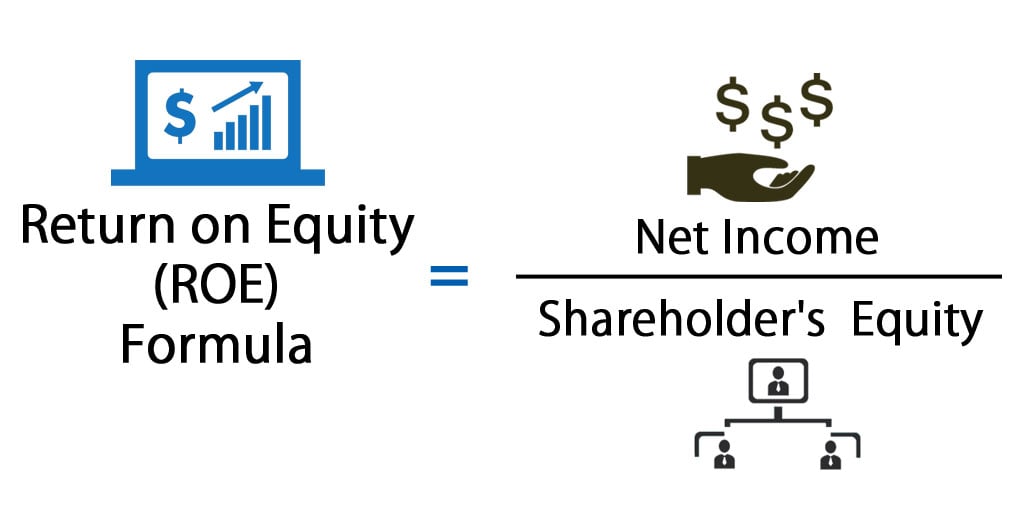
What does shareholders’ equity tell you about a company?
A higher market rate of return and future dividends could increase that return. This form of corporate finance is common for startups and businesses in growth mode. Shareholder equity (SE) is a company’s net worth and it is equal to the total dollar amount that would be returned to the shareholders if the company must be liquidated and all its debts are paid off. Thus, shareholder equity is equal to a company’s total assets minus its total liabilities.
Accounting
Shareholders’ equity is the residual claims on the company’s assets belonging to the company’s owners once all liabilities have been paid down. Once you’ve successfully closed an investment and want to start optimizing your cash flow, check out Rho. With corporate cards, expense management, and AP automation, Rho is the all-in-one business banking platform you need to take control of your finances and scale your business. Investors view companies with higher CoEs as safer investments, and lenders consider them lower risk. Businesses generally announce dividend distributions before they happen, sometimes several months before the dividends are paid. If a dividend schedule has not been announced, you can use the average dividends paid in past years.
These indicators could include price-to-earnings ratio, industry trends, and dividends paid or distributed to investors. Businesses have assets (resources owned or operated by the company that add to its economic value) and liabilities (debts or obligations that detract from its economic value). Shareholders’ equity indicates the money that would belong to the company’s owners and shareholders after it sold all of its assets and took care of all its liabilities. Also known as stockholders’ equity or owners’ equity, shareholders’ equity boils down to the total value of a company after it pays off all of its debts. To compute total liabilities for this equity formula, add the current liabilities such as accounts payable and short-term debts and long-term liabilities such as bonds payable and notes. Upon calculating the total assets and liabilities, company or shareholders’ equity can be determined.
Shareholders’ equity includes preferred stock, common stock, retained earnings, and accumulated other comprehensive income. Negative stockholders’ equity occurs when a company’s total liabilities are more than its total assets. An alternative calculation of company equity is the value of share capital and retained earnings less law firm accounting and bookkeeping 101 the value of treasury shares. If we rearrange the balance sheet equation, we’re left with the shareholders’ equity formula. It’s calculated using the current treasury bill (T-bill) rate or the long-term yield of government bonds. Due to their government backing, these are considered “safe” or “risk-free” investments.
The stockholders’ equity subtotal is located in the bottom half of the balance sheet. Stockholders’ equity is a vital metric to gauge a company’s financial well-being and value for its shareholders. After accounting for debts and obligations, it represents the company’s net worth and ownership stake.




